| Calories | A calorie is a unit of energy. In nutrition and everyday language, calories refer to energy consumption through eating and drinking and energy usage through physical activity. |
|---|
| Fat | Fat is an essential part of our diet and nutrition, we cannot live without it. |
|---|
| Saturated Fat | Eating foods that contain saturated fats raises the level of cholesterol in your blood. |
|---|
| Cholesterol | Cholesterol is a waxy substance that comes from two sources: your body and food. |
|---|
| Sodium | Sodium is an element that the body needs to work properly. Salt contains sodium. |
|---|
| Carbohydrate | Carbohydrates are one of the main types of nutrients. They are the most important source of energy for your body. |
|---|
| Dietary Fiber | Helping to maintain a healthy weight and lowering your risk of diabetes and heart disease |
|---|
| Sugar | Sugar is an important part of the human diet, making food more palatable and providing food energy. |
|---|
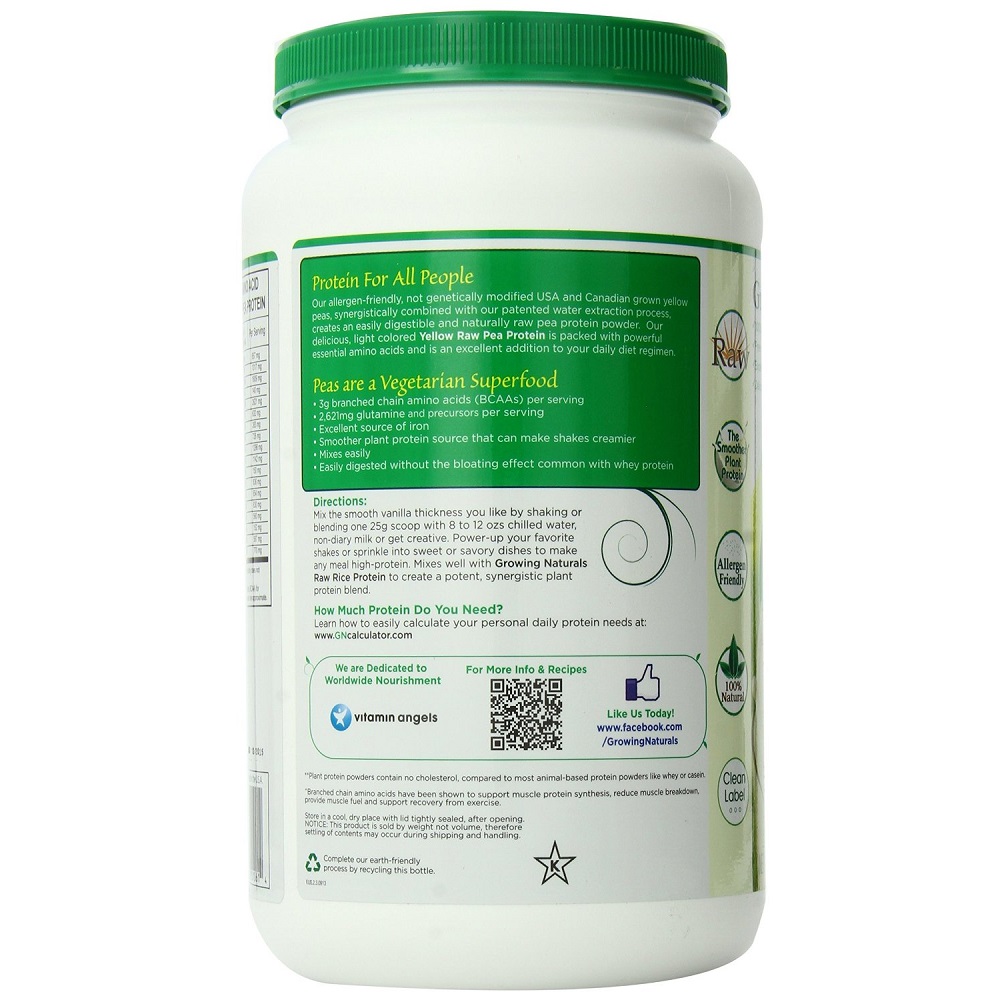
| Protein | They are essential in the diet of animals for the growth and repair of tissue. |
|---|
| Vitamin A | Vitamin A, also called retinol, helps your eyes adjust to light changes when you come in from outside and also helps keep your eyes, skin and mucous membranes moist. |
|---|
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C is an antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables. It is important for your skin, bones, and connective tissue. It promotes healing and helps the body absorb iron. |
|---|
| Calcium | Calcium is a mineral that is an essential part of bones and teeth. The heart, nerves, and blood-clotting systems also need calcium to work. |
|---|
| Iron | Iron is a mineral that is naturally present in many foods, added to some food products, and available as a dietary supplement. |
|---|
| Yellow Pea Protein | Pea protein is an animal-free supplement made from extracting the soluble pea protein from yellow split peas. |
|---|
| Coconut Sugar | Coconut sugar (also known as coco sugar, coconut palm sugar or coco sap sugar) is a sugar produced from the sap of cut flower buds of the coconut palm. |
|---|
| Whole Grain Brown Rice | Brown rice is a natural wholesome food rich in essential minerals such as manganese,iron, zinc, phosphorous, calcium, selenium, magnesium and potassium. |
|---|
| Vanilla Flavor | Vanilla extract (Vanilla Planifolia Andrews) is a liquid form of vanilla concentrate commonly used in cooking and baking. |
|---|
| Organic Stevia | Stevia is an intensely sweet natural sweetener that is harvested around the world from the stevia rebaudiana plant. |
|---|
| Alanine | Alanine (abbreviated as Ala or A) is a non-polar α-amino acid, with the formula CH3CH(NH2)COOH. |
|---|
| Arginine | L-arginine is a chemical building block called an amino acid. It is obtained from the diet and is necessary for the body to make proteins. |
|---|
| Aspartic Acid | L-aspartic acid, often just called aspartic acid, is an amino acid — the building block of proteins and necessary for several other processes in the body. |
|---|
| Cystine | A crystalline amino acid occurring in most proteins, esp. the keratins: yields two molecules of cysteine on reduction. |
|---|
| Glutamic Acid | Glutamic acid (abbreviated as Glu or E; encoded by the codons GAA or GAG) is an ɑ-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. |
|---|
| Glycine | Glycine is an amino acid, a building block for protein. It is not considered an “essential amino acid” because the body can make it from other chemicals. |
|---|
| Histidine | L-Histidine is an amino acid. People use histidine for medical purposes. |
|---|
| Isoleucine | Isoleucine is necessary for hemoglobin formation and in stabilizing and regulating blood sugar and energy levels. |
|---|
| Leucine | L-Leucine plays a central role in the metabolism of muscle tissue therefore contributing to both its generation and preservation. |
|---|
| Lysine | L-lysine is an amino acid (a building block of protein) that is essential for health. |
|---|
| Methionine | Methionine is an amino acid. Amino acids are the building blocks that our bodies use to make proteins. |
|---|
| Phenylalanine | Phenylalanine is an amino acid, a “building block” of protein. |
|---|
| Proline | Proline, also known as L-proline, is an amino acid. It is non-essential because it can be synthesized by the body through the breakdown of L-glutamate, another amino acid. |
|---|
| Serine | Serine is classified as a nutritionally non-essential amino acid. Serine is critical for the production of the body’s proteins, enzymes and muscle tissue. |
|---|
| Threonine | Threonine is an amino acid. Amino acids are the building blocks the body uses to make proteins. |
|---|
| Tryptophan | Tryptophan is an amino acid needed for normal growth in infants and for nitrogen balance in adults. |
|---|
| Tyrosine | Tyrosine is a nonessential amino acid the body makes from another amino acid called phenylalanine. |
|---|
| Valine | L-Valine is an essential amino acid and, along with L-Leucine and L-Isoleucine, is part of the branched chain of amino acids. |
|---|





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.