Ingredients
- Click on any Ingredient below to learn more about it at NutraWiki
| Calories | A calorie is a unit of energy. In nutrition and everyday language, calories refer to energy consumption through eating and drinking and energy usage through physical activity. |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrate | Carbohydrates are one of the main types of nutrients. They are the most important source of energy for your body. |
| Dietary Fiber | Found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes — is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation. |
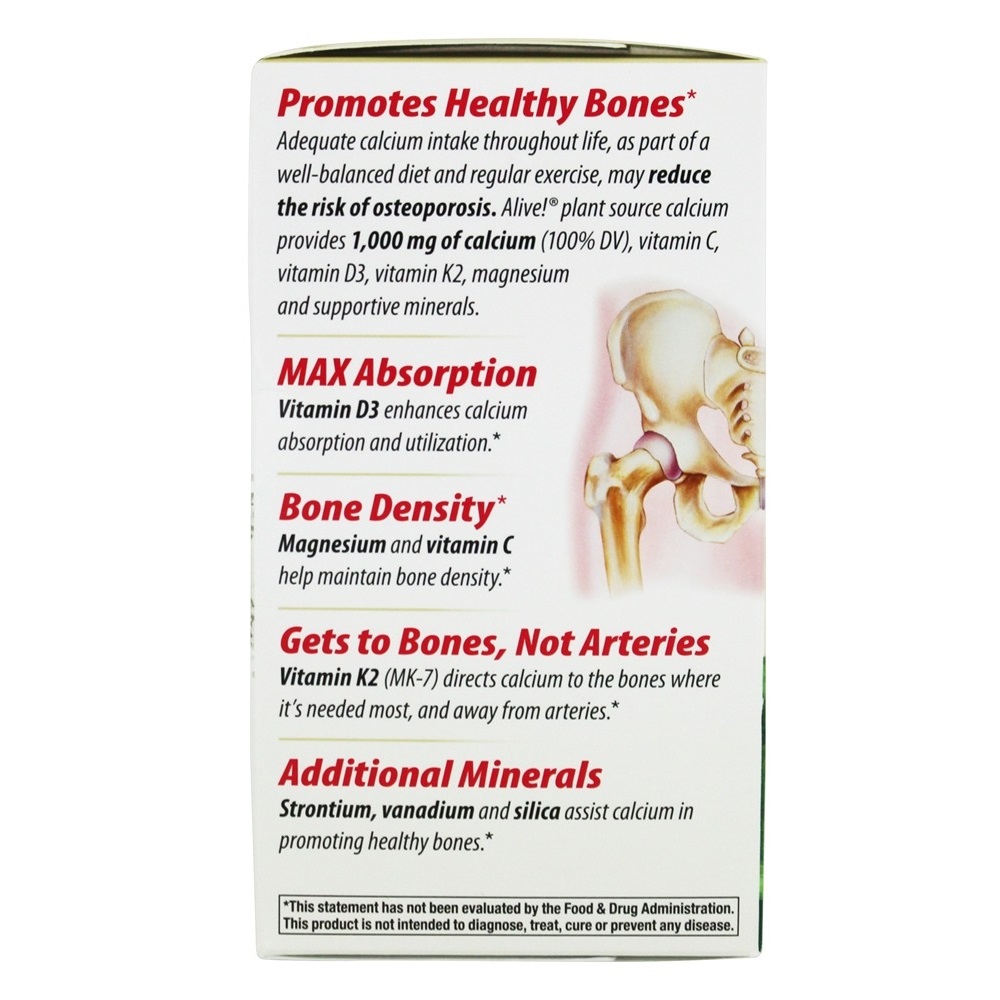
| Vitamin C | Vitamin C is an antioxidant found in fruits and vegetables. It is important for your skin, bones, and connective tissue. It promotes healing and helps the body absorb iron. |
| Vitamin D3 | Vitamin D3 can be taken as a supplement to improve overall health or used to treat osteoporosis. |
| Vitamin K2 | Vitamin K2 is an essential vitamin that many people never hear of until they have their first child and the nurse administers a Vitamin K injection. |
| Calcium | Calcium is a mineral that is an essential part of bones and teeth. The heart, nerves, and blood-clotting systems also need calcium to work. |
| Magnesium | Magnesium is required for the proper growth and maintenance of bones. Magnesium is also required for the proper function of nerves, muscles, and many other parts of the body. |
| Sodium | Is an element that the body needs to work properly. |
| Silica | Increasing bone mineral density when obtained from foods. |
| Boron | Boron is used for building strong bones, treating osteoarthritis, as an aid for building muscles and increasing testosterone levels, and for improving thinking skills and muscle coordination. |
| Vanadium | Vanadium is a mineral. It was named for the Norse goddess of beauty, Vanadis, because of its beautiful colors. Vanadium supplements are used as medicine. |
| Cellulose | Cellulose provides structure and strength to the cell walls of plants and provides fiber in our diets. Although some animals, such as ruminants, can digest cellulose, humans cannot. |
| Stearic Acid | Stearic acid is one of many fatty acids that occur naturally in various plants and animal derivatives. It’s found in such products as animal tallow, cocoa butter and vegetable fats. When it’s used in cosmetic products, stearic acid primarily fulfills the role of a thickener or hardener. Stearic acid is the substance that helps your bar of soap retain its shape — just as it does in products such as candles, oil pastels and hard candies. |
| Cellulose Gum | It’s a highly useful additive that acts as a stabilizing and thickening agent. |
| Citric Acid | Powerful Antioxidant - May Help Fight Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Sodium bicarbonate(IUPAC name: sodium hydrogen carbonate) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. |
| Modified Cellulose | Modified celluloses, also known as methylcellulose (MC) and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), are versatile, multifunctional food gums. |
| Maltodextrin | Maltodextrin is a starch-derived food additive that is commonly used as a thickening or filling agent in a range of commercial foods and beverages. |
| Silica | Increasing bone mineral density when obtained from foods. |
| Vegetable Glycerin | Glycerin is what is called a humectant. Glycerin helps maintain the skin’s water balance on an intercellular level. Glycerin in lotions or other skin care products can help prevent or combat dry skin. |






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.